Hypertension: A Silent Killer
Hypertension, often referred to as high blood pressure, is a silent killer that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a condition where the blood exerts excessive pressure on the walls of your arteries. If left untreated, hypertension can increase your risk of heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and other serious health complications.
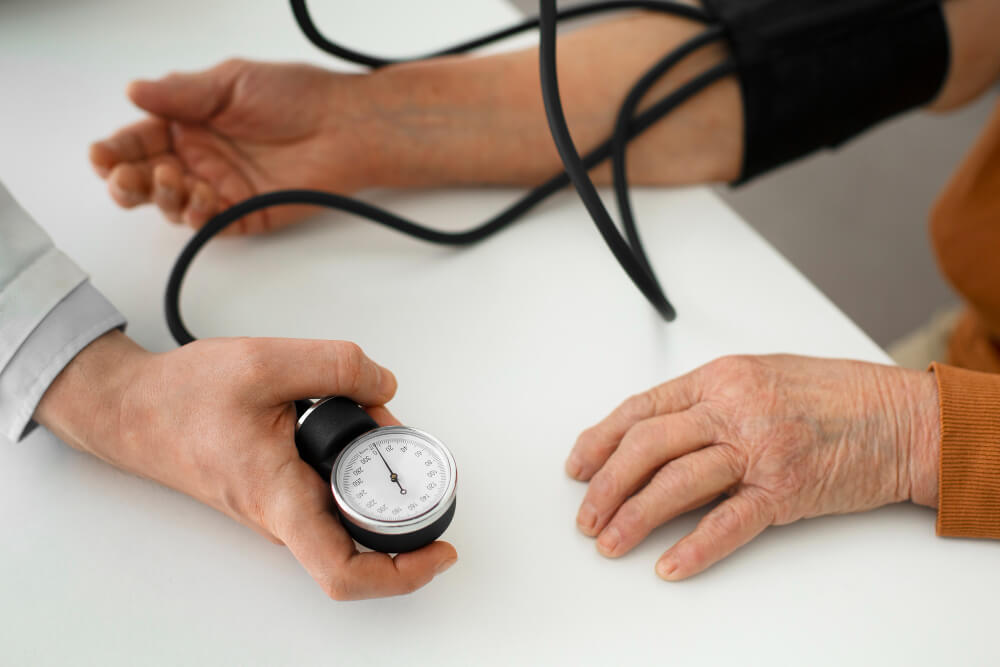
Understanding Hypertension
Hypertension is a chronic condition that develops over time. It is often asymptomatic, meaning that many people are unaware they have it until it is diagnosed during a routine check-up.
Types of Hypertension
There are two main types of hypertension:
- Primary Hypertension: This is the most common type and has no identifiable underlying cause.
- Secondary Hypertension: This type is caused by an underlying medical condition, such as kidney disease or thyroid problems.
Causes of Hypertension
The exact causes of primary hypertension are not fully understood, but several factors are believed to contribute:
- Genetics A family history of hypertension can increase your risk.
- Lifestyle Factors Unhealthy lifestyle choices, such as a poor diet, lack of exercise, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption, can contribute to hypertension.
- Medical Conditions Certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, thyroid disorders, and sleep apnea, can also cause hypertension.
Symptoms of Hypertension
High blood pressure often has no symptoms, which is why it is sometimes called the “silent killer.” However, in some cases, high blood pressure can cause headaches, dizziness, shortness of breath, or nosebleeds.
Diagnosis of Hypertension
Hypertension is diagnosed through regular blood pressure checks. Your doctor will use a blood pressure cuff to measure your blood pressure on multiple occasions.
Treatment for Hypertension
The treatment for hypertension depends on the severity of your condition and any underlying medical conditions. It often involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medications.
Lifestyle Modifications Making lifestyle changes can be highly effective in managing hypertension. These changes may include:

- Healthy Diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Weight Management: If you are overweight or obese, losing weight can help lower your blood pressure.
- Stress Management: Practicing relaxation techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can help reduce stress.
- Limited Alcohol Consumption: Moderate alcohol consumption is generally safe, but excessive alcohol intake can raise blood pressure.
- Quitting Smoking Smoking damages blood vessels and can raise blood pressure.
Medications In some cases, medications may be necessary to control high blood pressure. These may include:
- Diuretics
- Beta-blockers
- ACE inhibitors
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs)
- Calcium channel blockers
Monitoring Hypertension
Regular follow-up with your doctor is essential for managing hypertension. Your doctor will monitor your blood pressure and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Home Blood Pressure Monitoring
Your doctor may recommend using a home blood pressure monitor to track your blood pressure between office visits.
Complications of Untreated Hypertension
Untreated hypertension can lead to serious health complications, including:
- Heart Attack
- Stroke
- Kidney Disease
- Aortic Aneurysm
- Vision Problems
Hypertension is a serious health condition that can have significant consequences if left untreated. By making lifestyle changes and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can effectively manage your blood pressure and reduce your risk of complications.
