Comprehensive Adult Healthcare: A Focus on Diabetes Management
Diabetes, a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, affects millions of adults worldwide. Effective management of diabetes is crucial for preventing complications and maintaining overall health. This article explores the essential components of adult healthcare focused on diabetes prevention, early detection, treatment, and ongoing care.
Understanding Diabetes
Diabetes is primarily classified into two main types:
Type 1 Diabetes An autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
Type 2 Diabetes The most common type, characterized by insulin resistance, where the body doesn’t effectively use insulin.
Both types of diabetes require careful management to prevent complications.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of diabetes is crucial for preventing or delaying complications. Regular health checkups, including blood sugar tests, are essential for identifying prediabetes and type 2 diabetes.
- Risk Factors: Family history, obesity, sedentary lifestyle, and age are risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
- Symptoms: While type 1 diabetes often presents with sudden symptoms, type 2 diabetes may develop gradually with symptoms like increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision.
The Role of Preventive Care
Preventive care plays a vital role in diabetes management. Regular check-ups, including blood pressure monitoring, cholesterol tests, and eye exams, are essential for early detection of complications.
Diabetes Management: A Comprehensive Approach
Effective diabetes management involves a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and self-care.
Medication:
Diabetes medications, including insulin, oral hypoglycemic agents, and other therapies, are prescribed based on the type of diabetes and its severity.
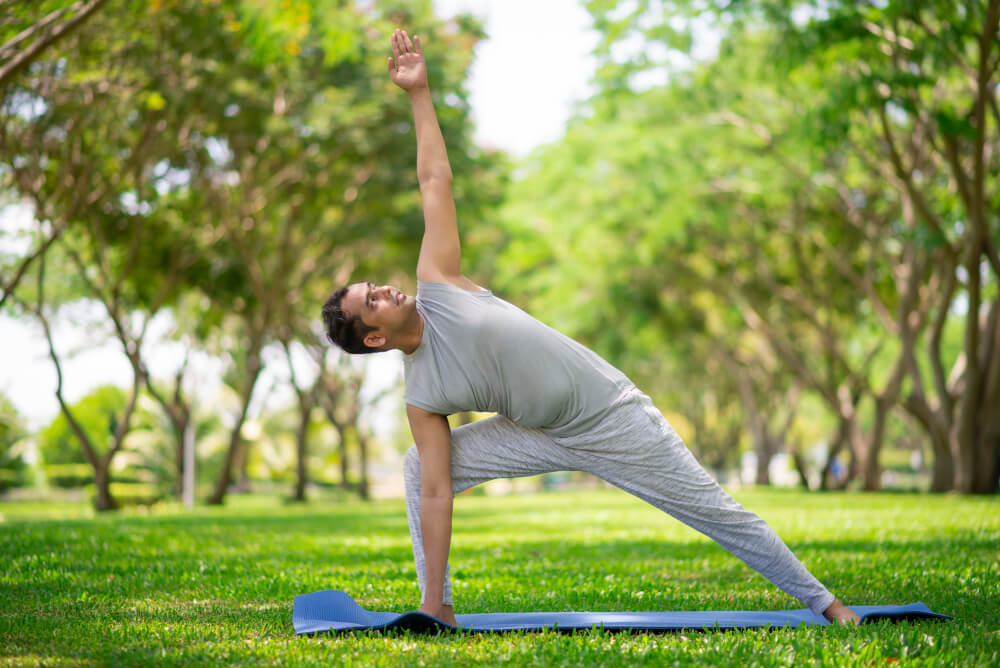
Lifestyle Modifications

- Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein is crucial for managing blood sugar levels.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for preventing and managing diabetes.
Self-Monitoring Regular :
Blood sugar monitoring is essential for making informed treatment decisions.
Diabetes Complications and Prevention
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to serious complications, including:
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Kidney disease
- Nerve damage
- Eye problems (diabetic retinopathy)
- Foot problems
By following a comprehensive diabetes management plan, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing these complications.
The Role of the Healthcare Team
A multidisciplinary approach is often necessary for effective diabetes management. Healthcare providers, including primary care physicians, endocrinologists, diabetes educators, dietitians, and podiatrists, work together to provide comprehensive care.
- Diabetes Educators: Provide education on diabetes self-management, including blood sugar monitoring, medication, and healthy lifestyle choices.
- Podiatrists: Specialize in foot care and can help prevent foot complications associated with diabetes.
- Ophthalmologists: Conduct regular eye exams to monitor for diabetic retinopathy.
- Nephrologists: Manage kidney disease if it develops.
Supporting Emotional Well-being
Living with diabetes can be challenging, and emotional support is essential. Healthcare providers should address the psychological impact of diabetes and offer counseling or support groups as needed.
By working closely with healthcare providers and adopting a proactive approach to diabetes management, individuals can lead fulfilling lives while effectively controlling their blood sugar levels.
